The Complex Journey of Aging
Aging is a multifaceted process resulting from complex changes in biological functions, ranging from DNA damage accumulation to protein dysfunction and altered intercellular communication. Our research focuses on deciphering these mechanisms at genomic, cellular, and systemic levels. This is the fundamental step towards identifying effective strategies to slow aging and enhance healthy lifespan.

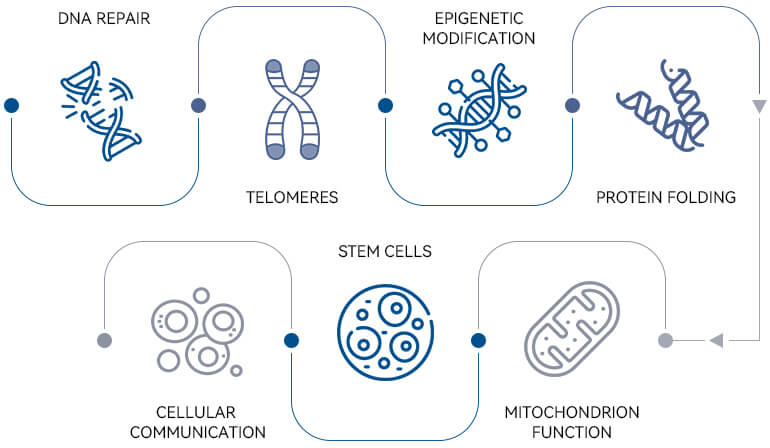
Hallmarks of Aging
Aging is driven by various biochemical changes occurring at different organismal levels, from molecular to systemic. Lopez-Otin and colleagues, in their influential 2013 publication in Cell, identified nine hallmarks of aging, which have become central to aging research and intervention. These hallmarks include Genomic Instability, Telomere Attrition, Epigenetic Alterations, Loss of Proteostasis, Deregulated Nutrient Sensing, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Cellular Senescence, Stem Cell Exhaustion, and Altered Intercellular Communication. For more details, please refer to the original paper at Cell.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
The Importance of NAD+
NAD+ and Anti-Aging
NAD+ is the scientifically proven anti-aging factor with ability to repair DNA damages, activate longevity proteins
Lifespan Boost in Animal Studies
NAD+ is a naturally existing coenzyme in all living cells and regulates hundreds of reactions
A Vital Coenzyme in Every Cell
The level of NAD+ declines with age, resulting in aging and increase of susceptibility to diseases
Therapeutic Potential of NAD+
The effects of extending life-span via NAD+ metabolism regulation have been proven in various model animals
NAD+ Decline with Age
NAD+ metabolism pathways as therapeutic targets has been investigated in various disease models
Clinically Proven Precursors
Clinical studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of NAD+ precursors (such as NMN, NR) in human




